Flute Synthesis
This project analyzes real flute recordings to figure out how to create a flute synthesizer.
Listen
| Real | Synthesized | |
|---|---|---|
| Single note | ||
| Duet |
Background
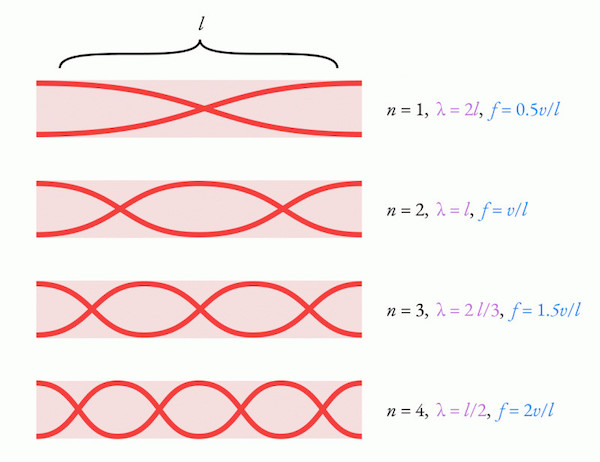
The flute is essentially an open air column, whose resonant frequencies come in integer multiples proportional to half the length of the instrument. Closing holes is a way of increasing the effective length of the instrument and decreasing the fundamental resonant frequency.
Additive harmonic synthesis
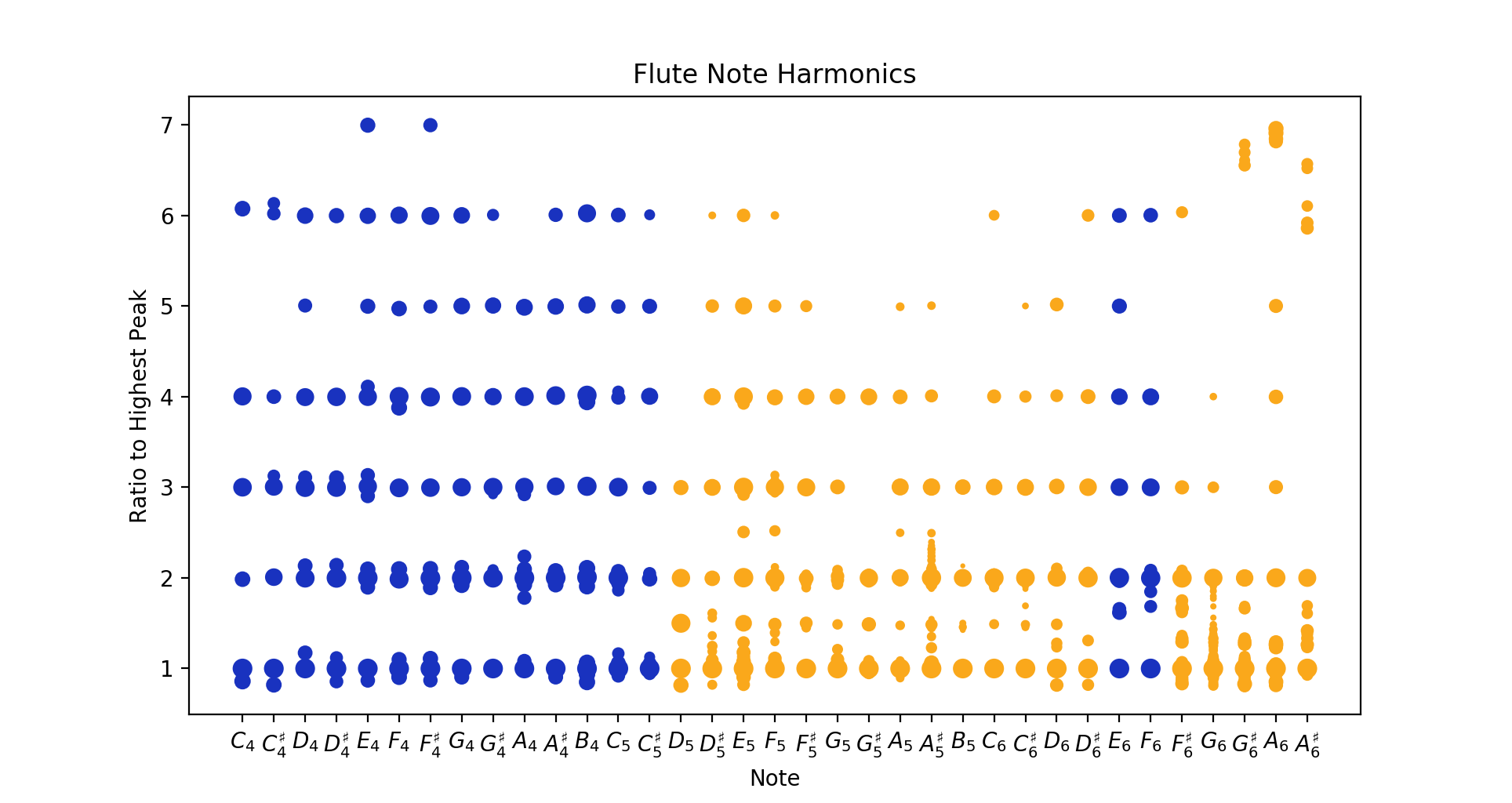
I picked the harmonics out of recordings of the flute to determine how much each component contributes. There is a visible split between regular and overblown notes, which are notes where the effective length of the instrument would produce a note an octave lower, but the air speed prevents the fundamental from sounding, leaving only the second and higher harmonics.
Subtractive noise component
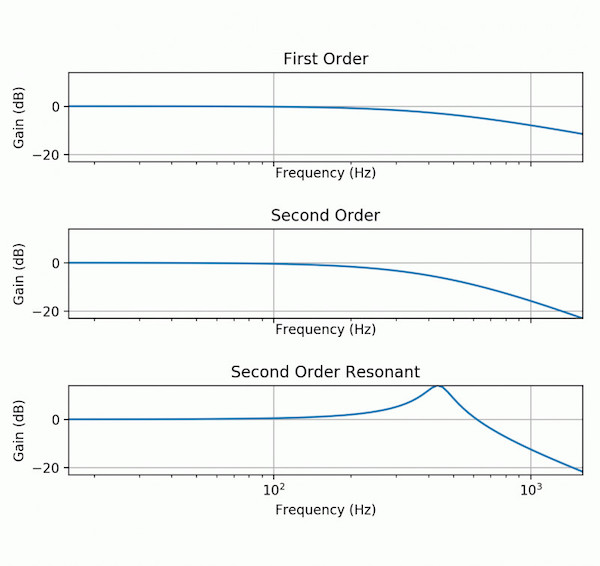
White noise is filtered using a resonant lowpass filter. This dampens the higher frequencies while leaving the low ones, while also increasing the amplitude around the cutoff frequency. This is an attempt to model the breathy sound of the flute, heard especially on the attack of a note, which is noisy, but resonates in the body of the instrument.
Vibrato
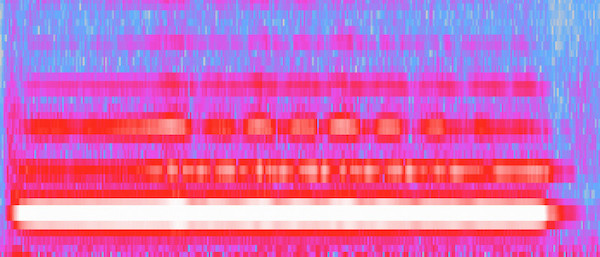
It is interesting that the "vibrato" in the flute is not technically vibrato in the traditional sense. Vibrato is defined as a modulation in pitch, but that is not what we see here. It makes sense that we would not see a change in pitch, since flute vibrato is done entirely with air flow, which does not change the length of the instrument and therefore does not bend the pitch. It also is not traditional tremolo, although this gets close. Tremolo is amplitude modulation, which is what we see, except that it only affects the upper harmonics. Upper harmonic tremolo is perhaps more accurately defined as brightness modulation since it primarily affects the timber of the sound.